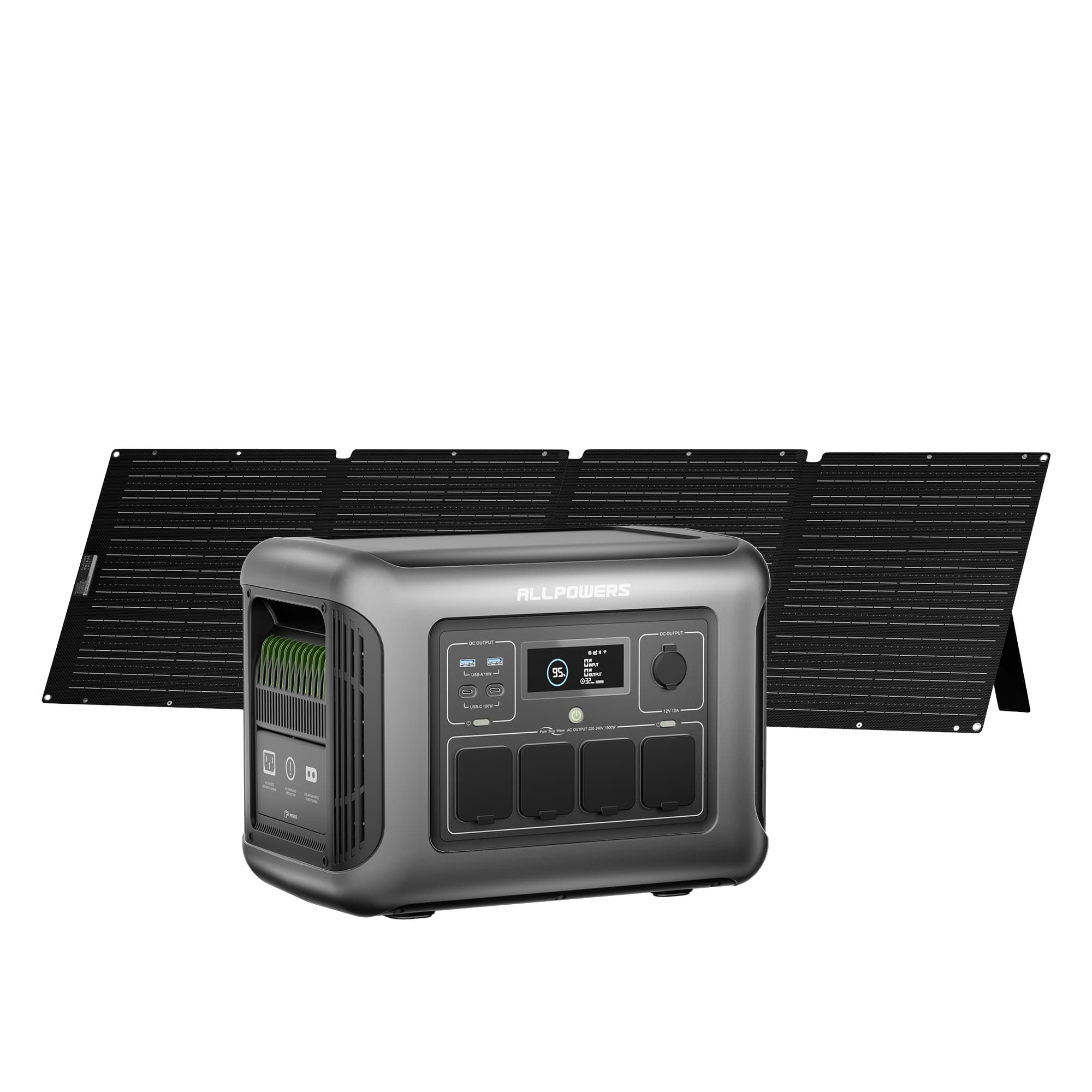
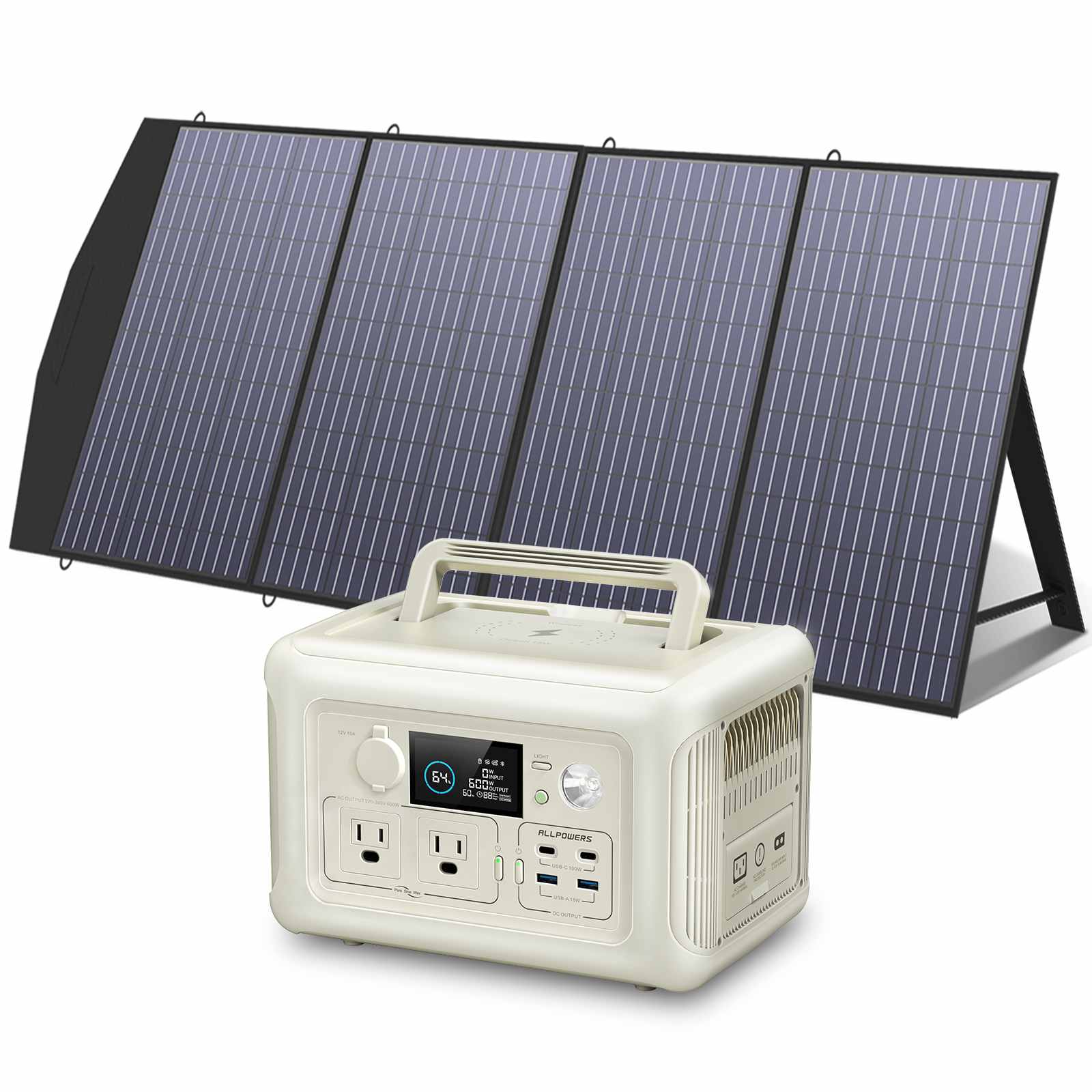
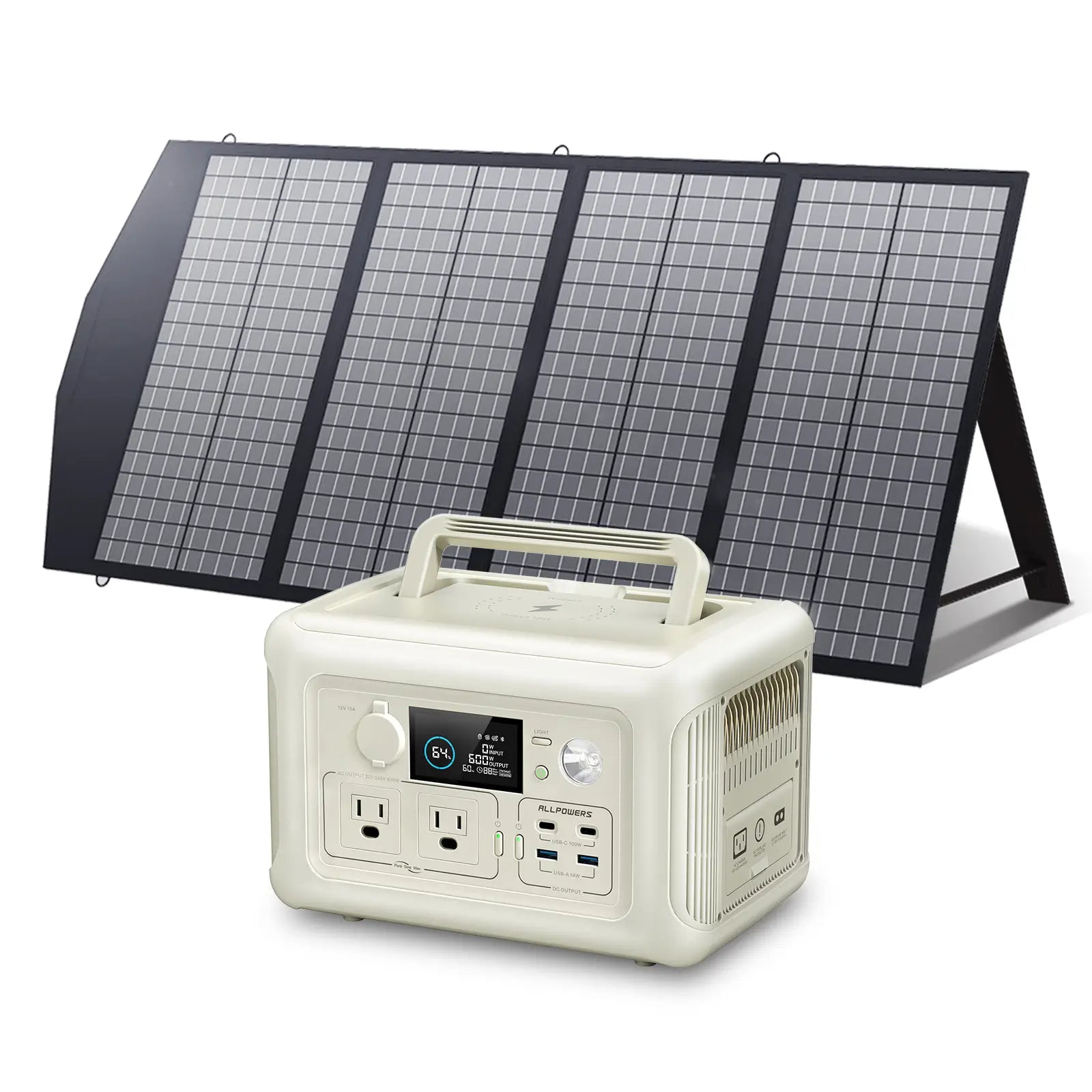
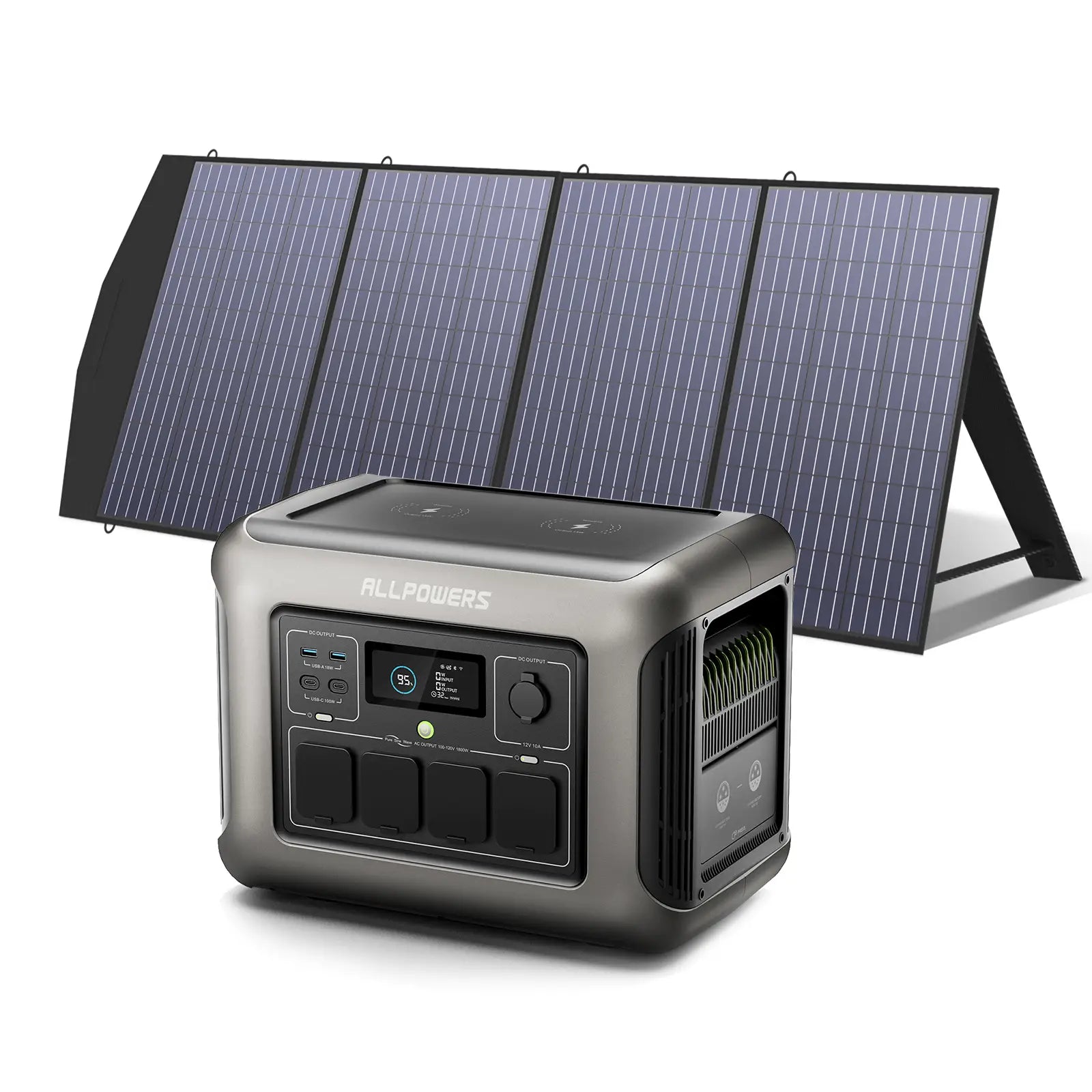
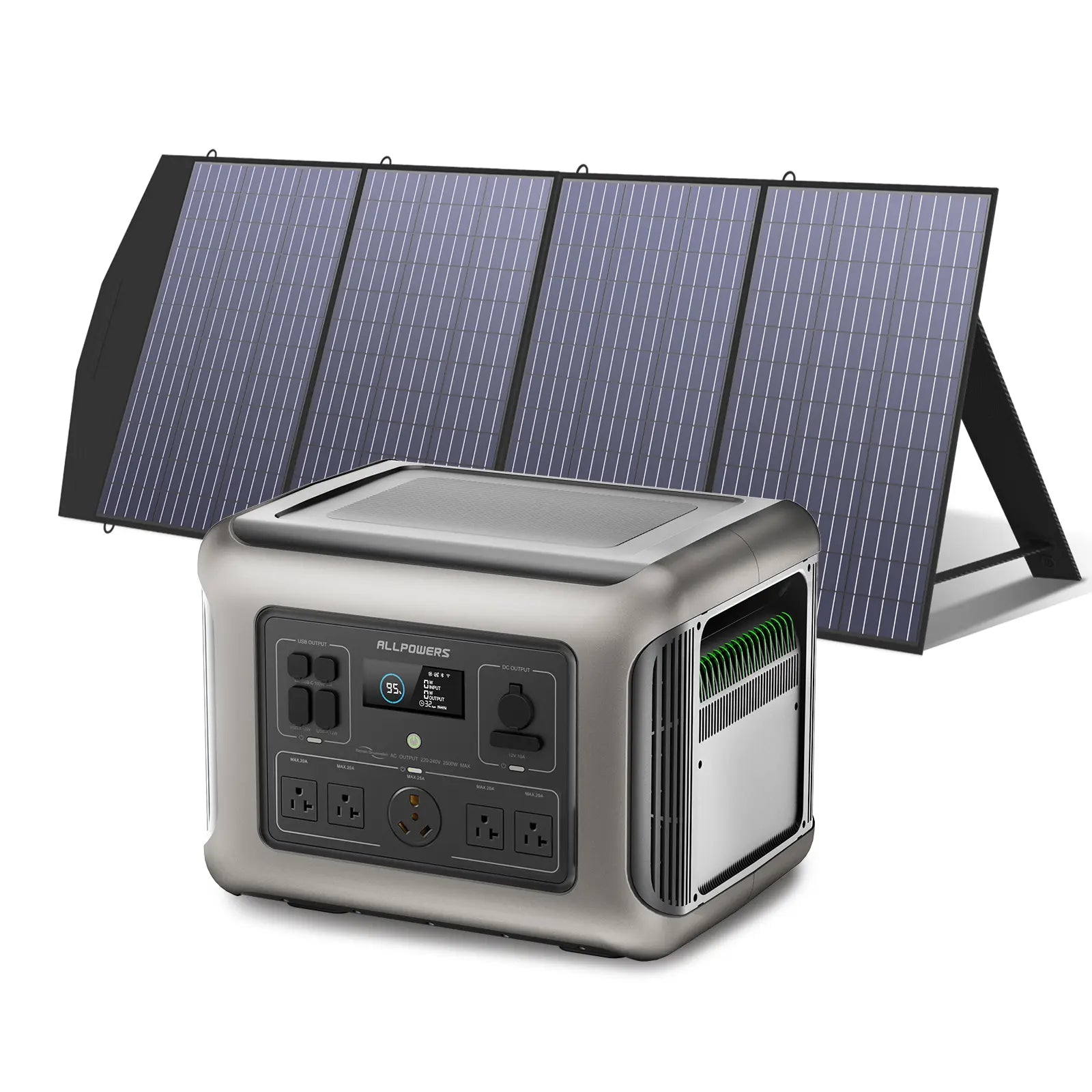
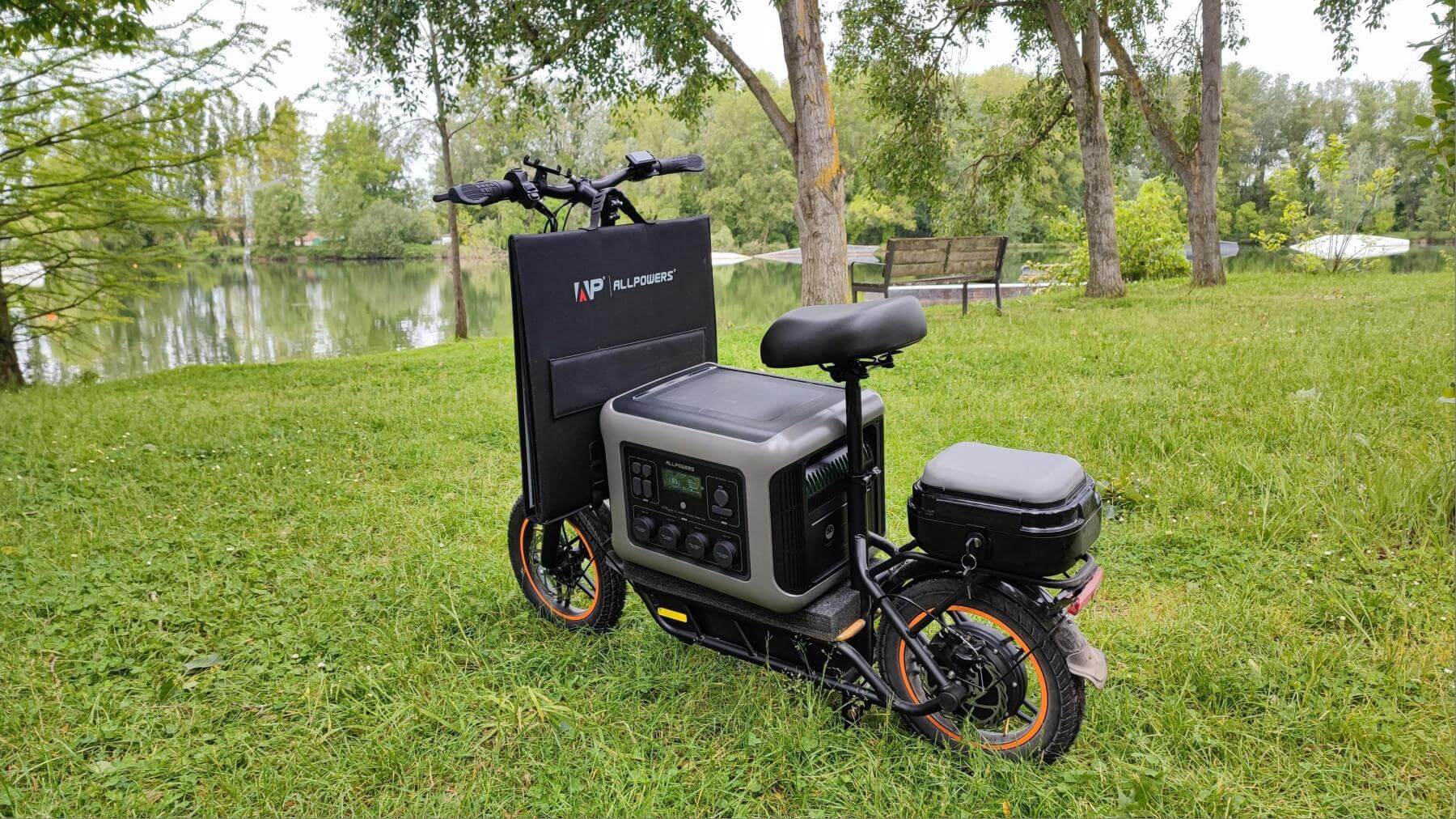
As e-bike technology evolves, riders are no longer confined to city commutes or short local loops.
Increasingly, cyclists are venturing onto longer mountain trails, deeper into forests, and embarking on multi-day tours far from the grid.
This growing desire for extended, off-grid riding necessitates reliable portable charging solutions.
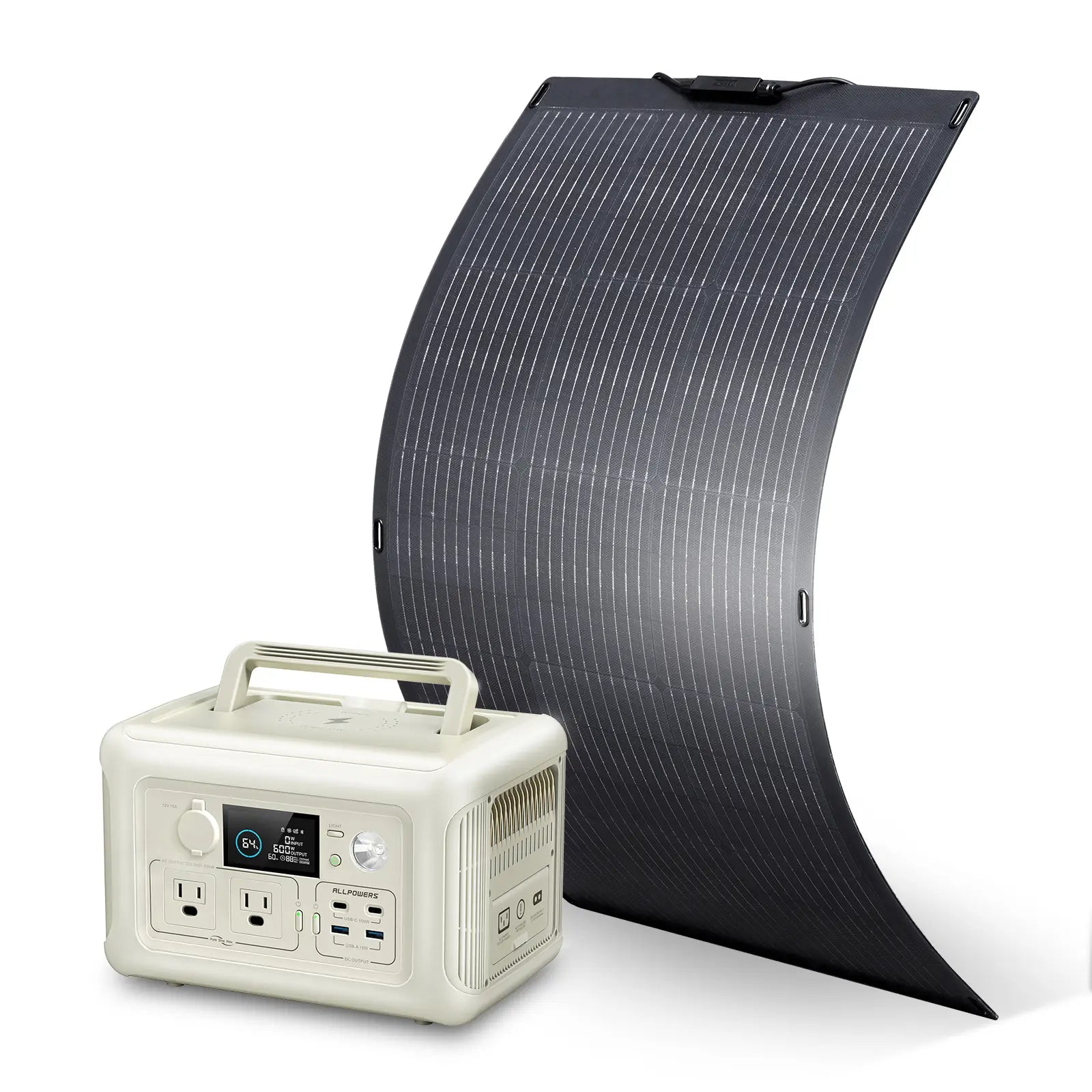
As one of the most popular off-grid energy sources, are portable power stations capable of recharging e-bikes to boost their range?
TL;DR:
Yes, a portable power station can charge an electric bike, and it’s often easier than people expect. The key is matching your e-bike charger’s wattage and voltage needs with the power station’s output and capacity. Most modern stations handle this without fuss.
How Much Power is Needed to Charge an Electric Bike?
First, let’s get a grip on what an e-bike actually needs during charging.
An electric bike usually comes with a removable lithium-ion battery somewhere between 250Wh and 750Wh, though high-power models can climb even higher.
The charger that connects it to the wall brings its own rating—maybe 2A, 3A, sometimes 4A—and that tells you how fast your bike is likely to charge.
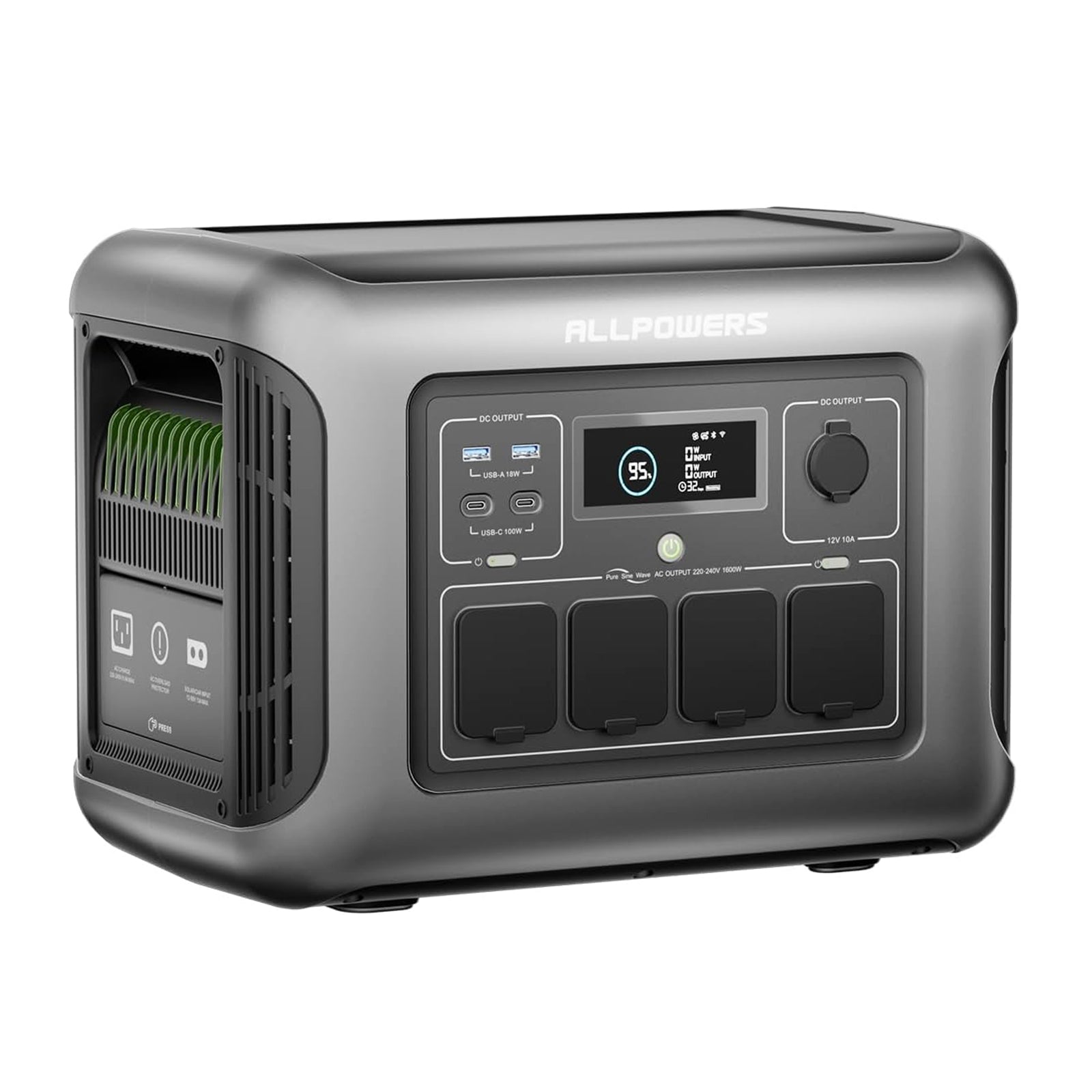
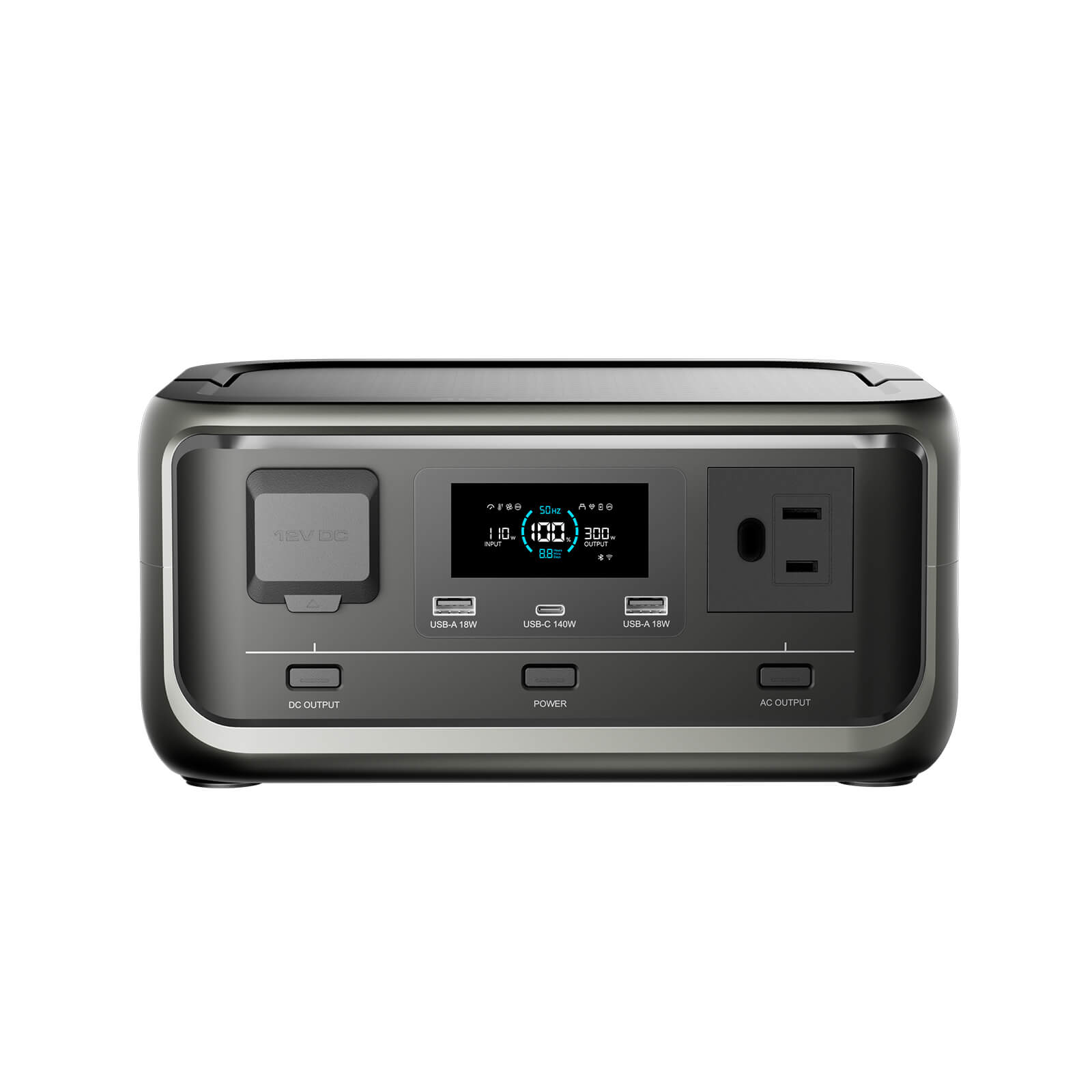
Most e-bike chargers run on standard AC power, usually between 100–240V. That’s the same type of output you get from a typical portable power station’s AC outlet.
If your bike charger says "54.6V 2A," that’s roughly 110W. A power station with a 300W AC inverter handles that easily.
But if someone’s running a fast charger—say 4A at 54.6V—that’s nearly 220W, which means they’ll want a power station comfortably above that threshold.
How Long a Portable Power Station Can Charge an E-Bike
Here’s the thing: even if the power station can supply the wattage, you also want to know how long it will last. So let’s talk through an example that mirrors typical use.
Say your e-bike battery is 500Wh. If your power station also has a 500Wh capacity, that doesn’t mean you’ll get a full charge.
Why? Energy losses. Converting DC to AC, heat from the charger, inefficiencies—all of it chips away.
On average, you’ll get roughly 70–80% of the rated capacity in real-world charging.
So that same 500Wh power station might realistically give you about 350Wh to 400Wh of usable charging before it’s drained.
That could bring your bike to about 60–70% from empty.
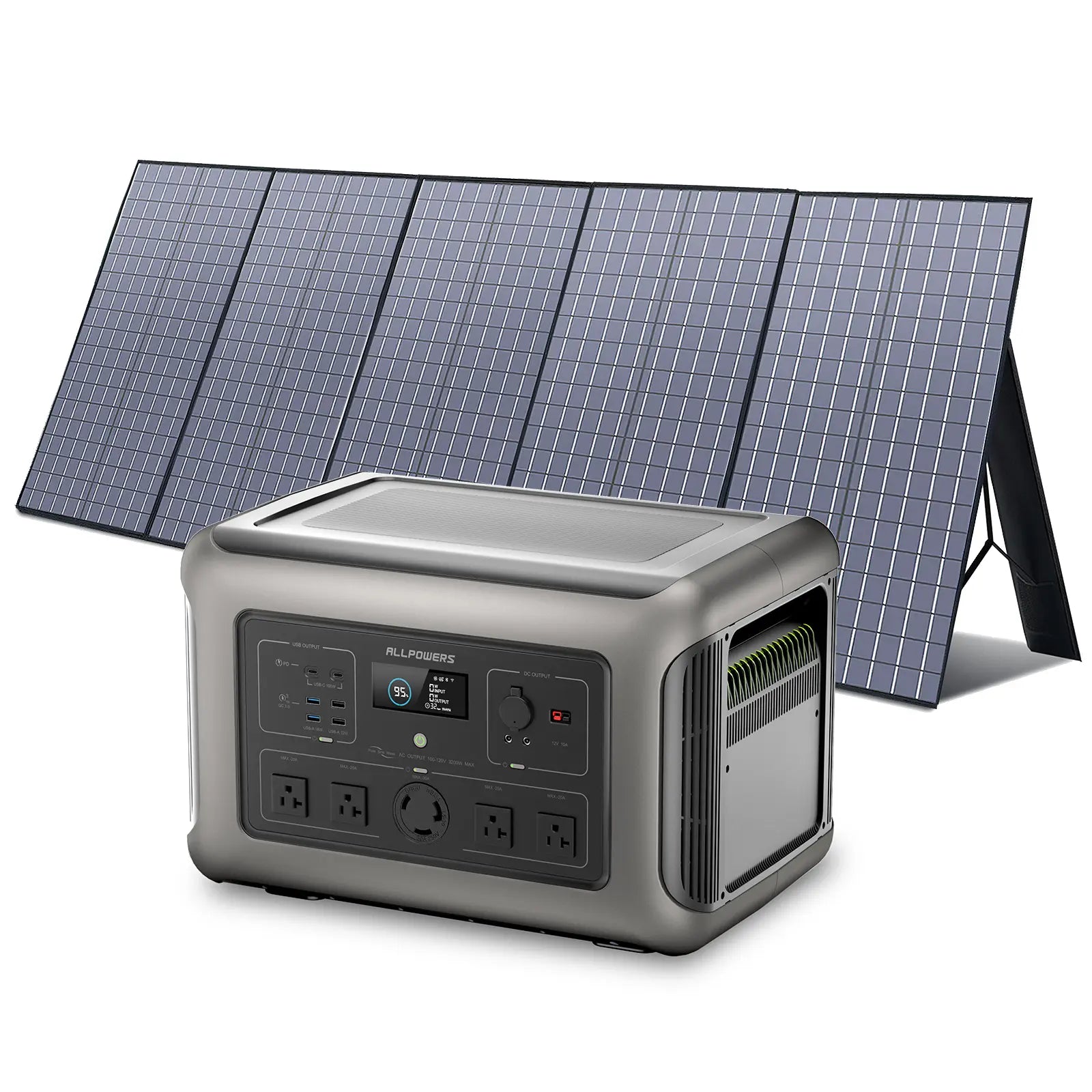
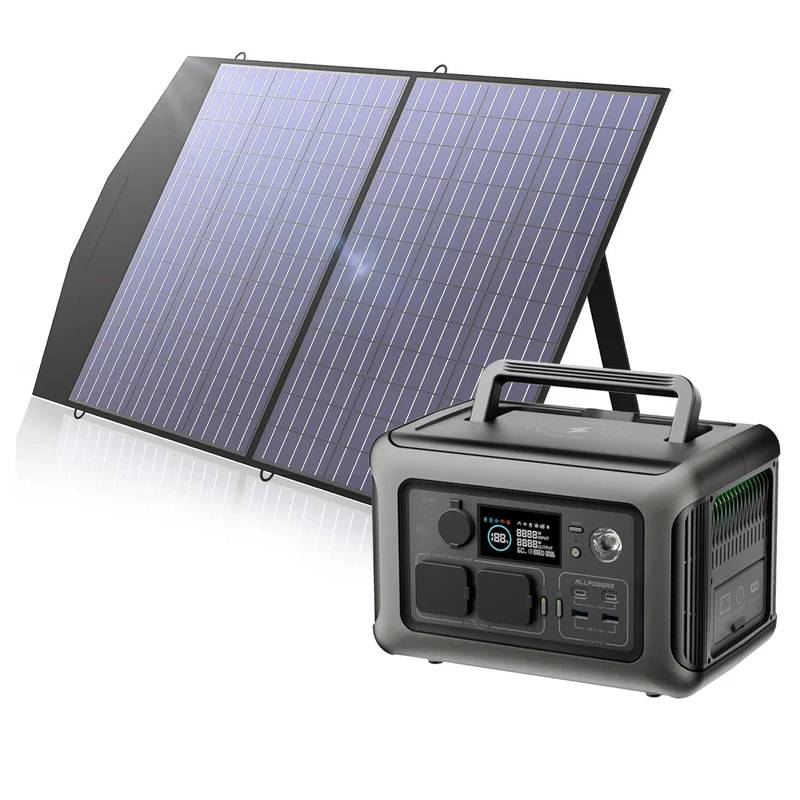
Not too bad, really. And if you add solar panels into the equation, you stretch your station’s usefulness dramatically.
This hybrid method is common among bikepackers who spend multiple nights outdoors.
How Fast Does an Electric Bike Charge From a Portable Power Station?
This hinges mostly on your e-bike charger. Portable power stations don’t speed up or slow down the charger; they simply supply the power.
If your charger is a 2A model, it’ll charge slowly—sometimes five to seven hours for a full battery.
If it’s a fast charger—say 4A or 5A—you’ll cut that time down significantly.
But keep in mind that faster chargers mean higher wattage, which means your power station drains quicker.
Charge times also depend on whether you’re topping off a partially drained battery.
A 30% to 80% refill is always quicker—e-bike BMS systems naturally slow down near the top to protect cell longevity.
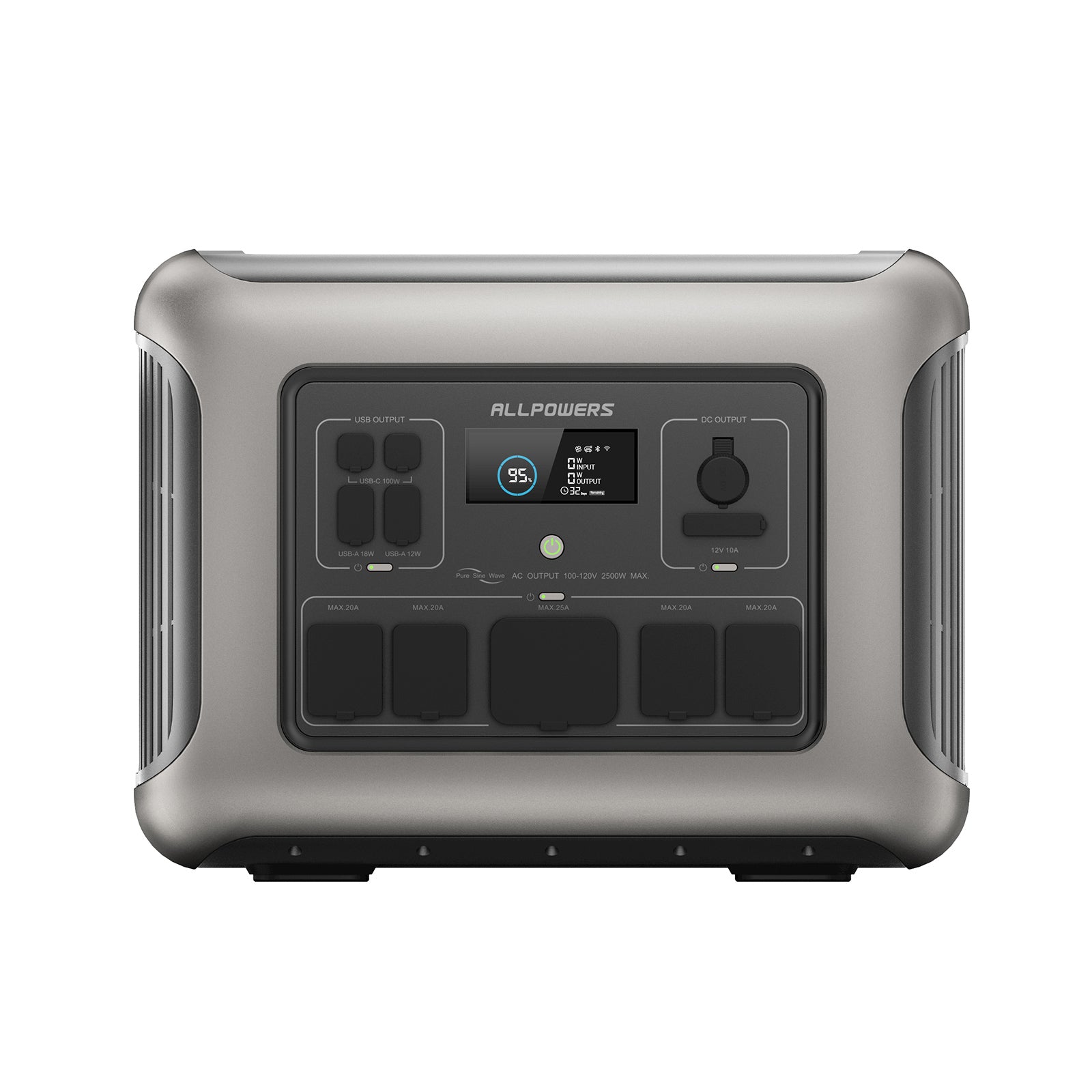
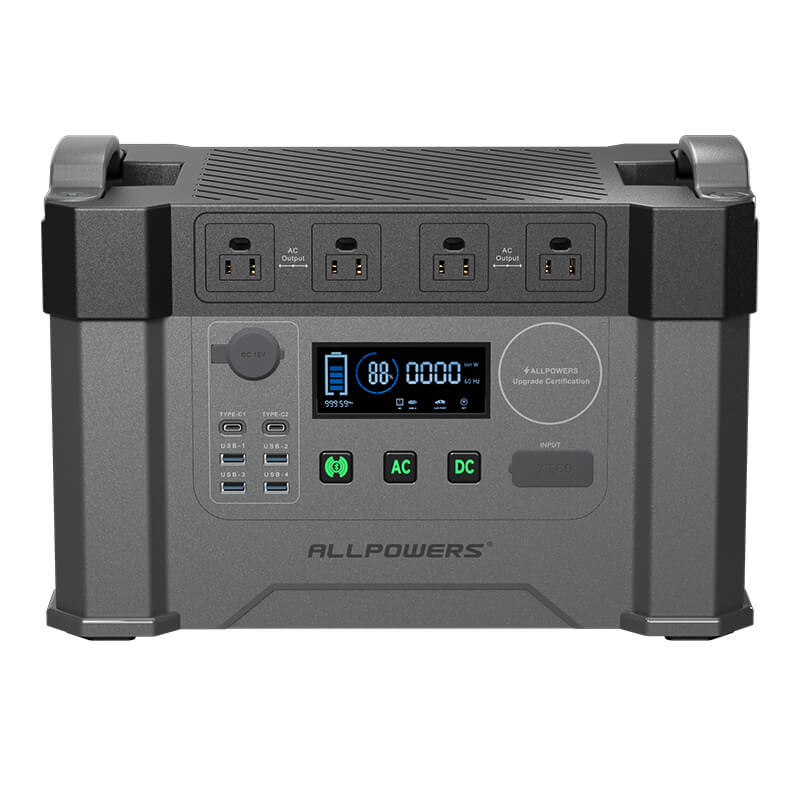
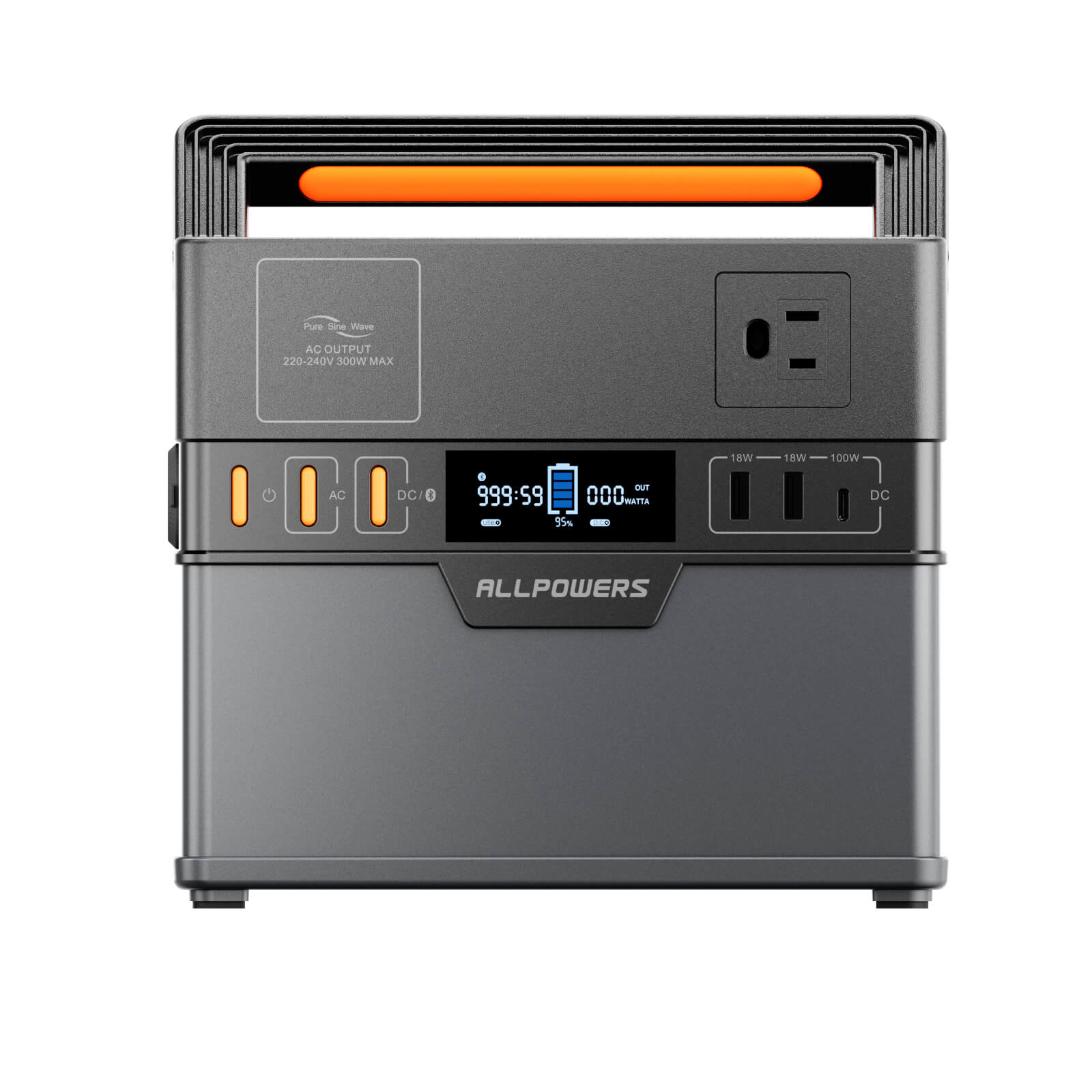
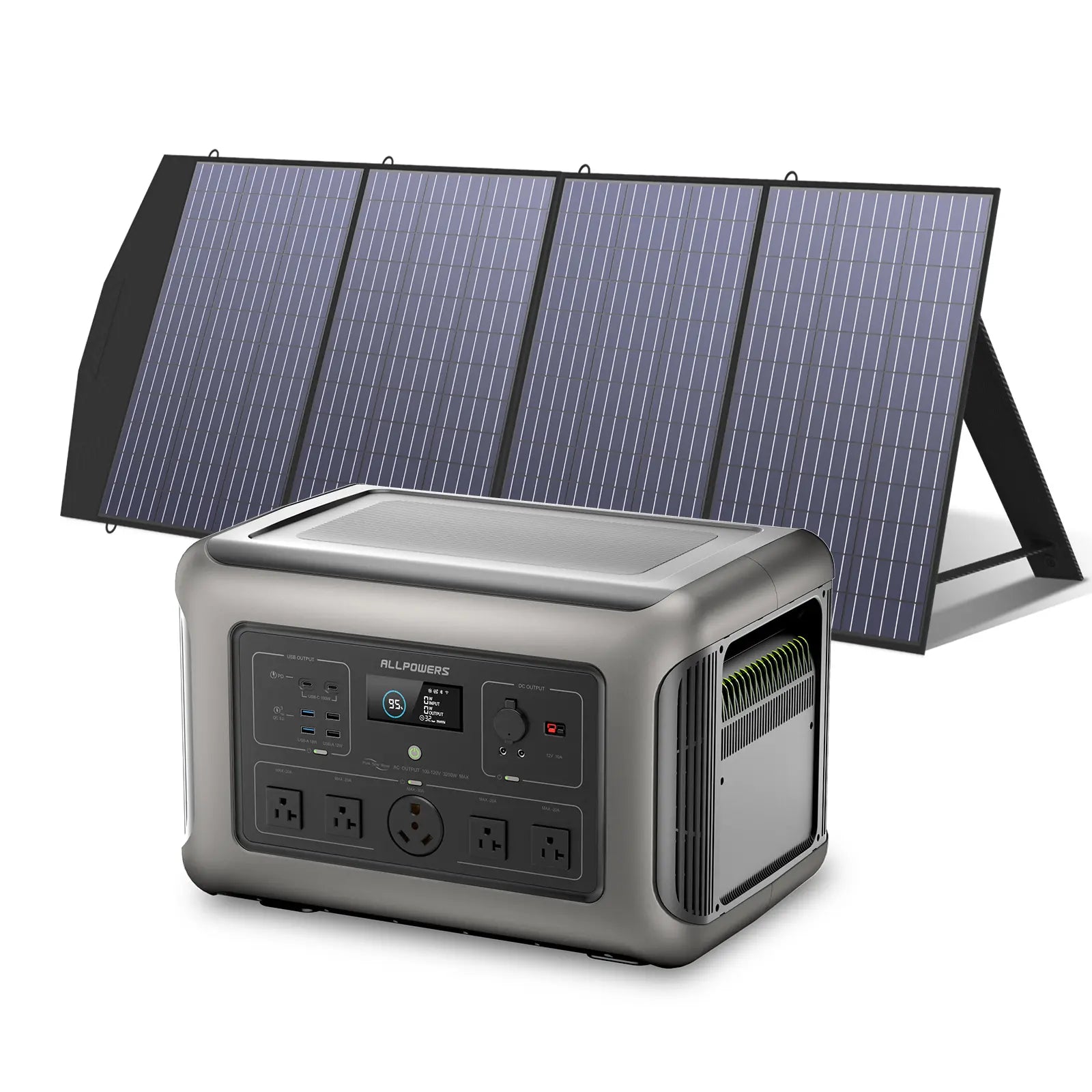
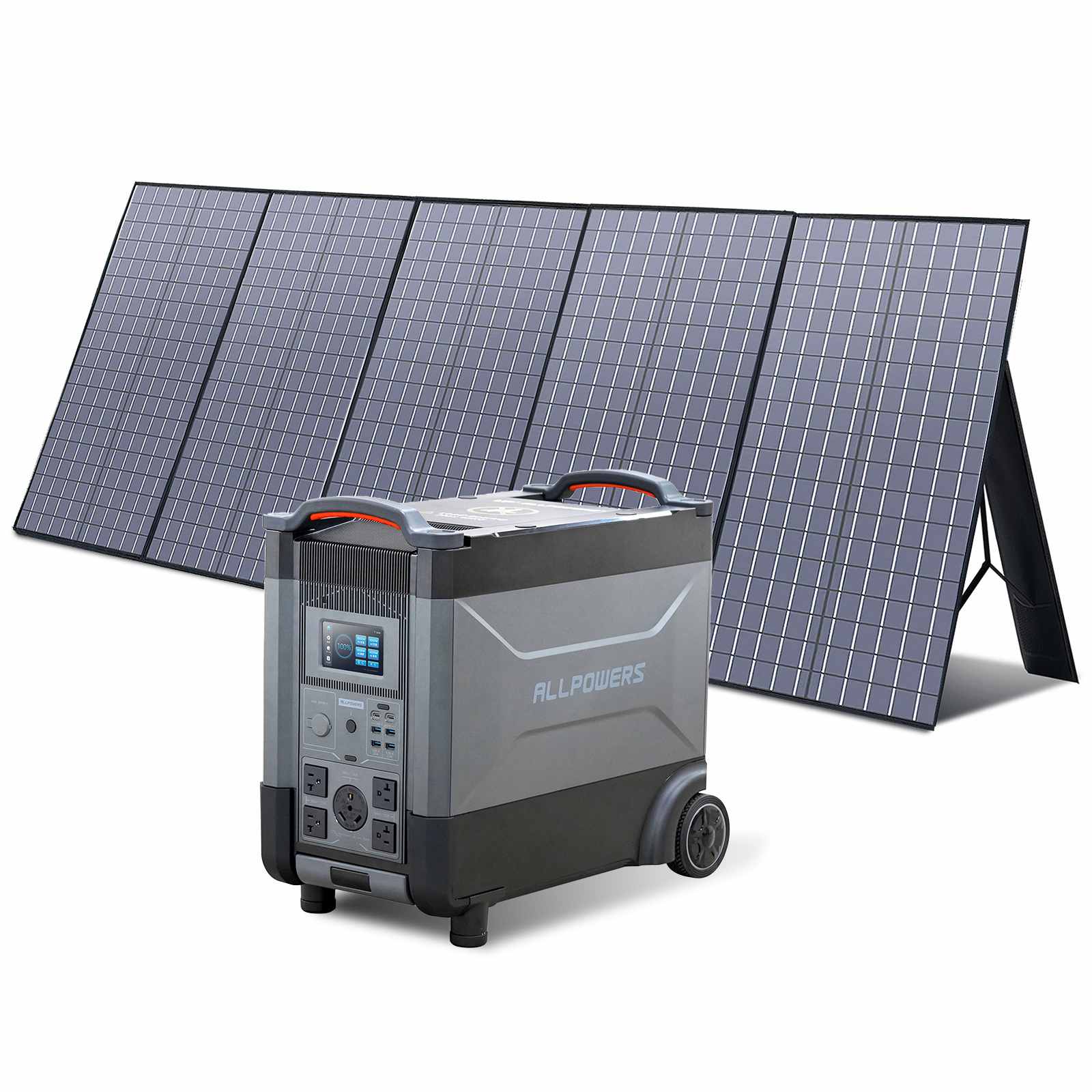
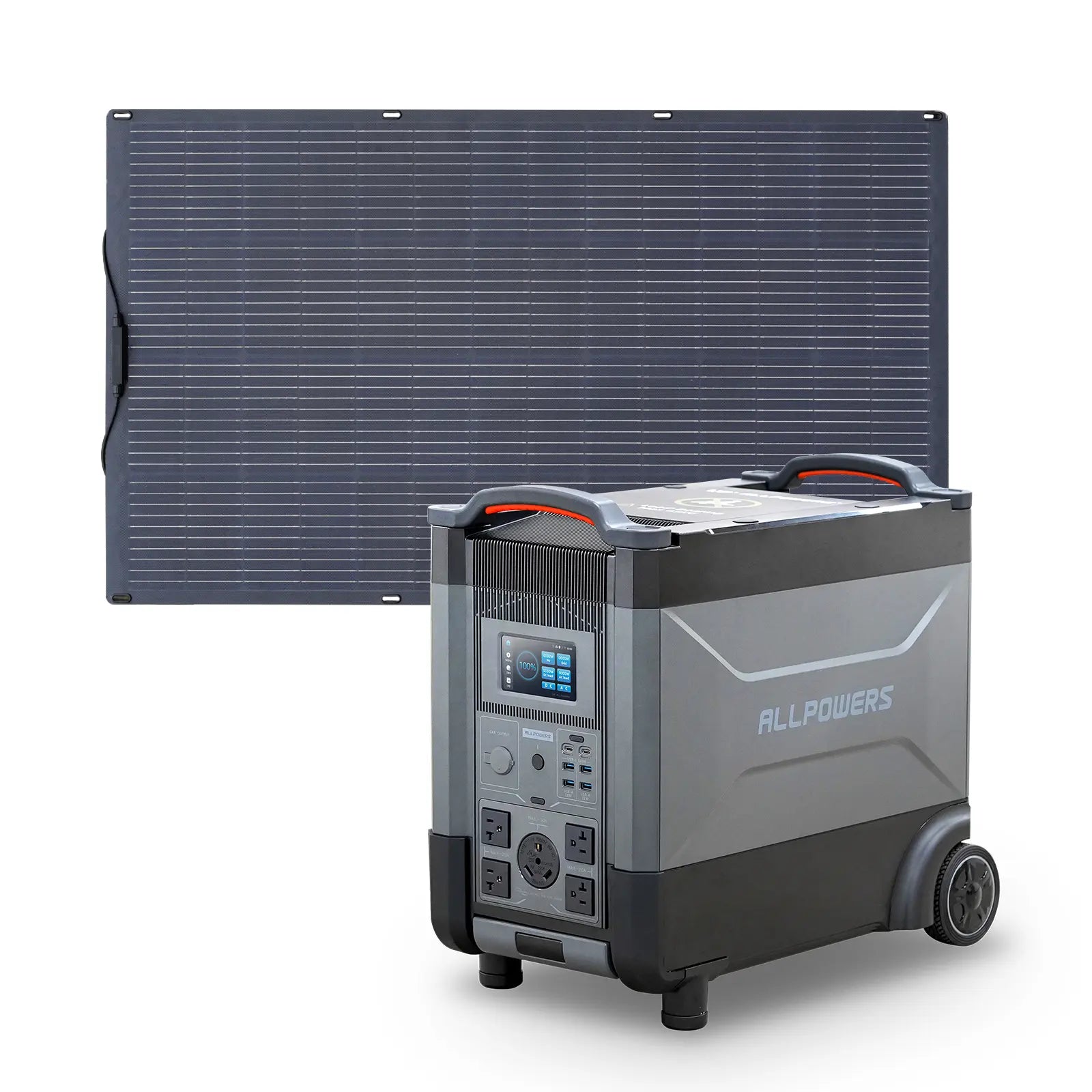
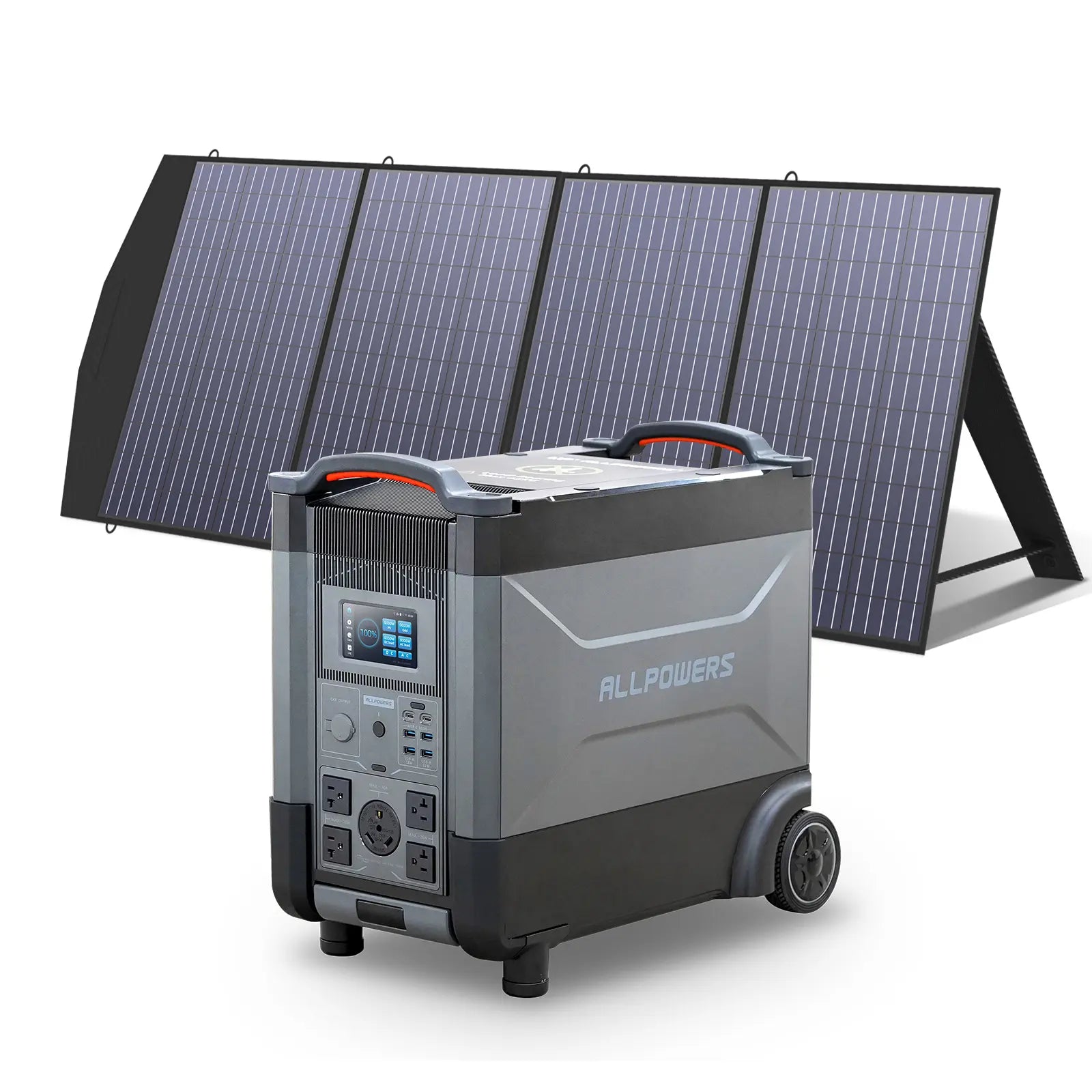
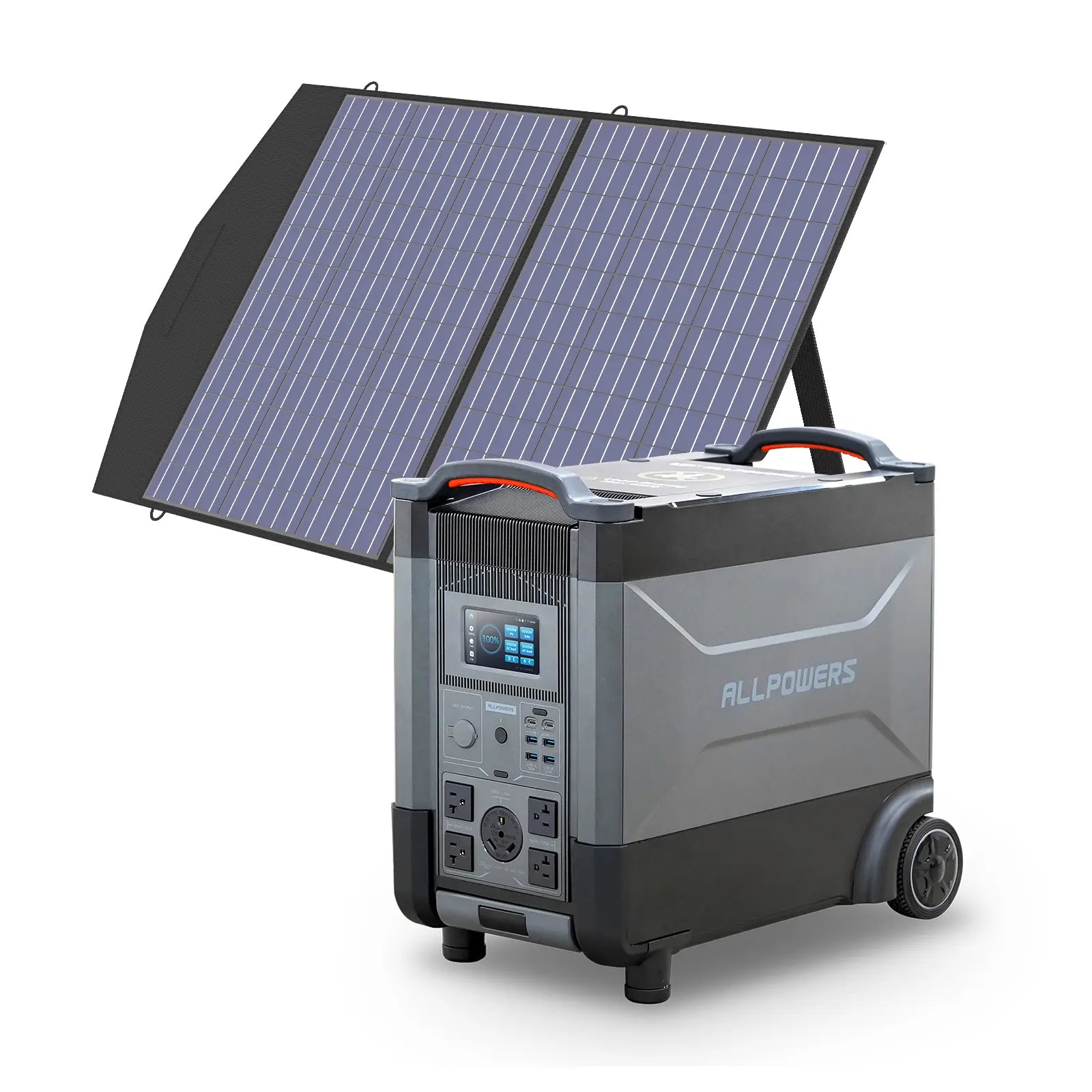
Choosing the Right Portable Power Station for Charging an E-Bike
You don’t need a huge, heavy energy brick to charge an e-bike. You only need a power station that matches your charging needs.
Look for sufficient AC output first. If your charger draws 200W, choose a power station delivering at least 300W. Then consider capacity. Do you want one full charge, two, or simply a backup for partial top-offs?
Portability matters, too. A lighter power station is easier to load into a vehicle or carry to a campsite. Even riders who love gear tend to appreciate something that doesn’t feel like hauling a car battery.
E-bike chargers typically require pure sine wave AC power. Some older or budget power stations use modified sine wave inverters, which can make chargers run hot or even refuse to operate.
Learn More: Pure Sine Wave Inverter Vs Modified Sine Wave Inverter
The last thing to consider is solar compatibility. If multi-day trips are your style, choosing a power station that accepts fast solar input feels smart.
Safety Considerations When Charging an E-Bike from a Portable Power Station
The good news is that modern portable power stations come with built-in protections: overcurrent, overvoltage, short-circuit, and high-temperature safeguards. But you still need to pay attention to a few simple things.
Your e-bike charger should always be the original one or a reputable replacement with proper certifications. Cheap, off-brand chargers increase the risk of thermal issues.
Avoid running the power station inside a sealed tent or tiny storage compartment if it’s working hard under high load. While they don’t produce fumes like fuel generators, they still warm up under heavy use.
And check your power station’s AC port rating before plugging in. Don’t guess — wattage mismatches trip overloads instantly and can confuse first-time users.
The truth is, charging from a portable power station is incredibly safe when matched correctly, because both devices use lithium technology already designed with tight tolerances.
Conclusion
So, can a portable power station charge an electric bike?
Absolutely.
And in many situations, it charges it just as reliably as a plug in the wall.
All you need is a power station with the right AC output, enough battery capacity, and a quality pure sine wave inverter.